GRC Framework: A Comprehensive Guide
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) Framework: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s complex business environment, organisations face numerous challenges related to governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC). To address these challenges effectively, many companies are adopting a GRC framework. This article provides an overview of the GRC framework, its components, and how to implement them.
What is a GRC Framework?
The GRC framework is a structured approach that helps organisations align their governance, risk management, and compliance activities with their business objectives. It provides a holistic view of the organisation’s risk profile, regulatory requirements, and internal controls, enabling better decision-making and risk mitigation.
Components of a GRC Framework
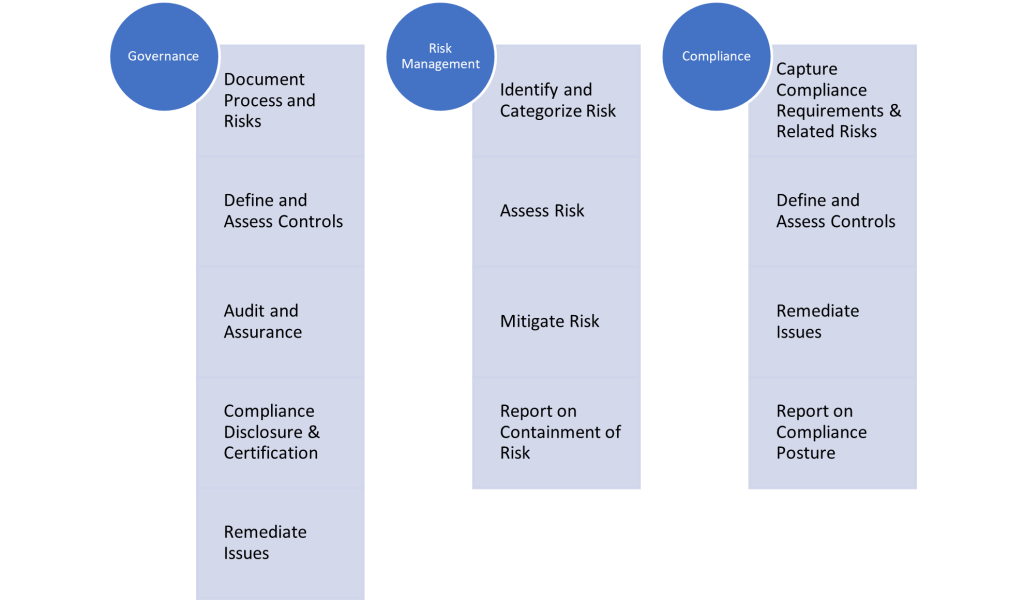
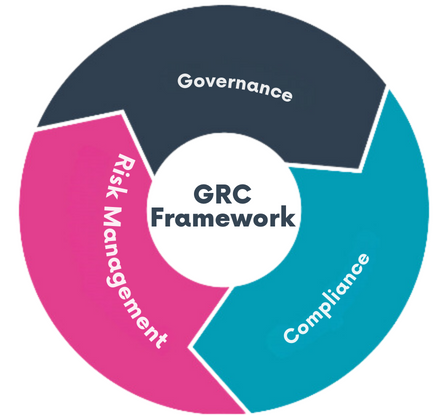
- Governance: Governance refers to the system of rules, practices, and processes by which an organisation is directed and controlled. It involves defining the organisation’s objectives, establishing policies and procedures, and monitoring performance to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and internal policies.
- Risk Management: Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and prioritising risks to the organisation’s objectives. It includes developing strategies to mitigate or avoid risks and monitoring the effectiveness of these strategies.
- Compliance: Compliance refers to the process of adhering to laws, regulations, standards, and internal policies relevant to the organisation’s operations. It involves ensuring that the organization is aware of its legal and regulatory obligations and implementing measures to meet those obligations.
- Previously, the term ‘GRC’ lacked a defined focus for managing the various types of risks, such as ESG, cyber, third-party risk, etc. However, as the scope of GRC is expanding, along with the growing complexity, velocity, and volume of risks, the management of ESG, cyber, TPRM, and other risks has evolved into distinct yet connected disciplines that are laser focused on managing the risks end-to-end.
- Support for complex organizational models with the ability to roll up at various organizational levels, while retaining the ability to cost-effectively deploy the solution within a department to enable a tactical compliance or risk initiative.
- Ability to support multiple regulations: corporate initiatives (SOX, risk management, ethics, policy compliance, etc.) as well as compliance initiatives (cGMP, HACCP, ISO 9000, GDPR, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, DORA, FCPA, Dodd Frank, etc.). It is critical that a GRC solution can support all governance, risk, and compliance management initiatives within a company. A wrong choice would force the organization to revert to having to support multiple point solutions.
- Integrated policy and document management capability that should cut across all GRC functions.
How to Implement a GRC Framework
Implementing a GRC framework involves several key steps:
- Assessment: Begin by assessing the organisation’s current governance, risk management, and compliance practices. Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the organisation’s objectives and how they align with its governance, risk management, and compliance goals.
- Develop Policies and Procedures: Develop policies and procedures that outline the organisation’s approach to governance, risk management, and compliance.
- Risk Identification: Identify and assess the organisation’s risks, including operational, financial, and compliance risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Develop strategies to mitigate or avoid risks, including implementing controls and monitoring mechanisms.
- Compliance Monitoring: Implement processes to monitor compliance with laws, regulations, and internal policies.
- Review and Improve: Regularly review the GRC framework to ensure its effectiveness and make improvements as necessary.
GRC Software and Tools
There are several GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) software and tools available in the market that can help organisations streamline their GRC processes and activities. These tools offer a range of features to support governance, risk management, compliance, and internal control activities. Here are some popular GRC software and tools:
- RSA Archer: RSA Archer is a widely used GRC platform that offers a comprehensive suite of tools for managing governance, risk, and compliance activities. It provides modules for risk management, policy management, incident management, and compliance management, among others.
- MetricStream: MetricStream is another popular GRC platform that offers a range of solutions for managing risk, compliance, and quality management processes. It provides modules for risk assessment, policy management, audit management, and regulatory compliance.
- ServiceNow GRC: ServiceNow GRC is a GRC platform that is integrated with the ServiceNow platform, allowing organizations to manage GRC processes alongside other IT and business processes. It offers modules for risk management, policy management, audit management, and compliance management.
- SAP GRC: SAP GRC is a GRC platform that integrates with SAP’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, allowing organizations to manage GRC processes within their existing SAP environment. It offers modules for risk management, access control, and compliance management.
- ACL GRC: ACL GRC is a GRC platform that offers solutions for managing risk, compliance, and audit processes. It provides modules for risk assessment, control monitoring, and audit management, among others.
- LogicManager: LogicManager is a GRC platform that offers solutions for managing risk, compliance, and policy management processes. It provides modules for risk assessment, control monitoring, and incident management.
Benefits of a GRC Framework
Implementing a GRC framework offers several benefits:
- Improved Decision Making: By providing a holistic view of risks and compliance requirements, a GRC framework helps organisations make informed decisions.
- Enhanced Risk Management: A GRC framework enables organisations to identify, assess, and mitigate risks effectively, reducing the likelihood of costly incidents.
- Better Compliance: By centralising compliance efforts, a GRC framework helps organisations stay compliant with laws, regulations, and internal policies.
- Increased Efficiency: A GRC framework streamlines governance, risk management, and compliance processes, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings.
What Are the Challenges of GRC?
While the GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework offers many benefits, implementing and maintaining it can pose several challenges for organisations:
- Complexity: GRC frameworks can be complex, especially for large organizations with diverse operations. Managing the interdependencies between governance, risk management, and compliance activities can be challenging.
- Integration: Integrating GRC processes and systems across the organization can be difficult. Different departments may have their own systems and processes, making it challenging to achieve a unified GRC framework.
- Resource Constraints: Implementing and maintaining a GRC framework requires dedicated resources, including personnel, technology, and budget. Many organizations struggle to allocate sufficient resources to GRC activities.
- Regulatory Changes: Keeping up with regulatory changes and ensuring compliance can be challenging. Regulations are constantly evolving, requiring organizations to adapt their GRC frameworks accordingly.
- Data Management: GRC relies heavily on data for risk assessments, compliance monitoring, and decision-making. Managing and analyzing large volumes of data can be challenging, especially if the organization lacks the necessary tools and expertise.
- Cultural Resistance: Implementing a GRC framework requires a cultural shift towards risk awareness and compliance. Resistance to change from employees and stakeholders can hinder the adoption of GRC practices.
- Silos: Siloed information and communication within organizations can hinder the effectiveness of GRC. Lack of collaboration and coordination between departments can lead to gaps in governance, risk management, and compliance.
- Technology Challenges: GRC relies on technology for data management, reporting, and automation of processes. Implementing and integrating GRC technology solutions can be complex and costly.
- Measurement and Reporting: Measuring the effectiveness of GRC activities and reporting on key metrics can be challenging. Organizations need to establish clear metrics and reporting mechanisms to track progress and demonstrate value.
- Emerging Risks: GRC frameworks may not always be equipped to handle emerging risks, such as cybersecurity threats, environmental risks, or geopolitical uncertainties. Organizations need to continuously assess and adapt their GRC frameworks to address new risks.
What Is the GRC Capability Model?
The GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) Capability Model is a framework developed by OCEG (Open Compliance & Ethics Group) that provides organizations with a structured approach to building and improving their GRC capabilities. It is designed to help organizations assess their current GRC maturity level and identify areas for improvement.
The GRC Capability Model consists of several key components:
- Core Capabilities: These are the foundational capabilities that form the basis of an effective GRC program. They include governance, risk management, compliance, and internal control.
- People, Process, and Technology: These are the three key components of a GRC program. People refer to the skills, knowledge, and competencies of individuals involved in GRC activities. Process refers to the procedures and workflows that govern GRC activities. Technology refers to the tools and systems used to support GRC activities.
- Integration: Integration refers to the alignment and integration of GRC activities across the organization. This includes integrating GRC with other business functions, such as finance, operations, and IT.
- Performance Measurement: Performance measurement involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to track the effectiveness of GRC activities. This helps organizations assess their GRC maturity level and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement involves regularly reviewing and enhancing GRC processes and practices to ensure they remain effective and aligned with business objectives.
Conclusion
A well-implemented GRC framework is essential for organisations looking to effectively manage governance, risk, and compliance. By aligning these functions with business objectives, organisations can enhance decision-making, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Read complete article about Best Cyber Practices .